Accessing New-Generation AI-Based Authoring Tools: Cognitive Boon or Bane for Engineering Education Pedagogy?
Former Associate Professor, Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology
[email protected]
Major Highlights
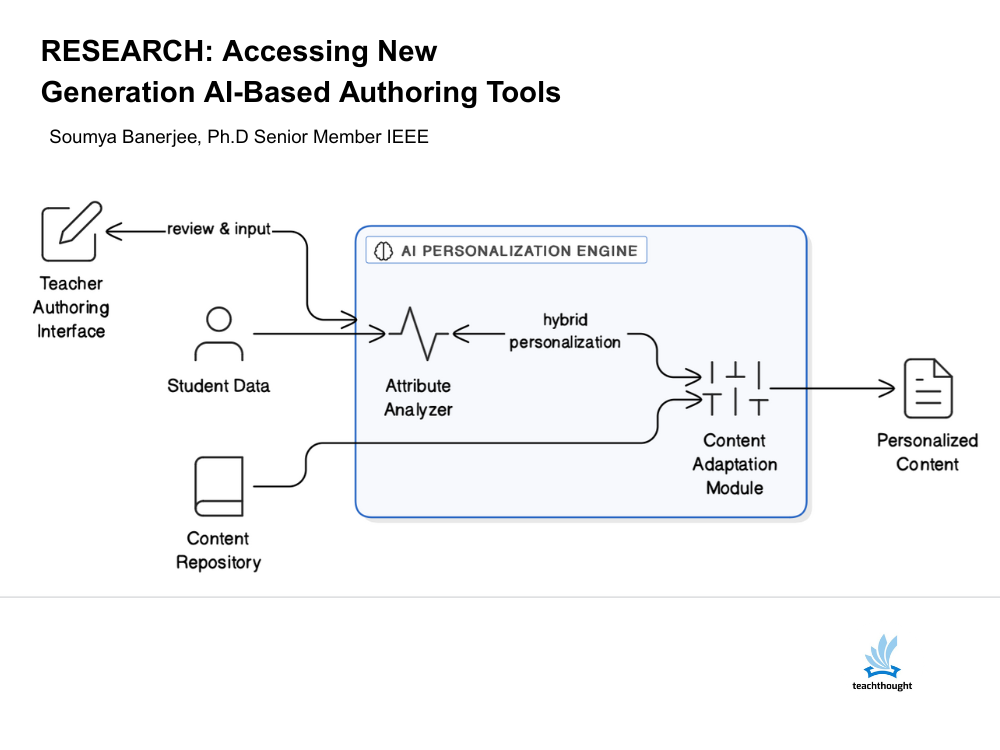
This article investigates current trends in AI-based authoring tools through a Large Language Model (LLM) lens, and evaluates how far they support personalized learning preferences, learning habits, and the emotional needs of higher-education students.
The article further examines key factors influencing the design of AI-based learning and authoring tools.
Finally, it outlines expected features of next-generation authoring platforms designed to more realistically map student attitudes and aptitudes.
Prologue
The academic domain has witnessed rapid progress in artificial intelligence (AI) and adjacent fields. This growth has accelerated the development of sophisticated tools and applications designed to support routine instructional needs—including content creation, scenario and simulation generation, automated assessments, and the cultivation of domain knowledge for students.
The impact of such AI-driven authoring tools has been particularly significant in engineering education, where cognitive and behavioral attributes shape learning outcomes. It remains necessary to critically evaluate the extent to which these tools can meaningfully contribute to cognitive development rather than merely automate it.
Within engineering education, the goal is not merely curriculum completion, but the cultivation of curiosity, autonomy, and conceptual depth. This article examines both the positive and limiting dimensions of AI-enabled authoring within conventional teaching and learning environments.
The remainder of this article is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews core characteristics of AI-based authoring tools, followed by analytical and performance-based perspectives on leading platforms in Section 3. Section 4 discusses the relationship between cognitive attributes and the design of authoring tools. Section 5 outlines potential future developments in AI-driven authoring systems.
Section 5 also addresses possible future enhancements that could enable more realistic cognitive alignment with learners through broader deployment of language-model-based authoring systems.
2. Essential Facts on AI-Driven Authoring Tools
E-learning authoring tools are software platforms used to create digital training content, including academic modules, assessments, simulations, and multimedia experiences—typically without requiring advanced coding skills. Content may be delivered through an LMS or directly to learners [3].
The core AI features reshaping conventional e-learning include:
- AI-assisted authoring
- Dynamic content creation
- Automated document rendering
- Content analytics and insights
Relevant techniques include procedural content generation (PCG) [19], AI-driven paraphrasing and summarization systems (e.g., QuillBot) [3], and recent advances in document parsing and document layout analysis (DLA) [4].
In summary:- Natural Language Processing (NLP): automates writing tasks including articles, reports, and structured academic text.
- Machine Learning (ML): enables personalized recommendations and adaptive pathways.
- Content Curation Systems: tailor materials based on learner behavior.
- Image Recognition: streamlines media classification and use.
- Voice Recognition: accelerates transcription and multimodal authoring.