What Are The Best Strategies For Teaching With Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Six practical strategies for using Bloom’s Taxonomy to design learning that moves beyond recall and encourages deeper, transferable thinking. Includes links to core Bloom’s resources and examples.
Keywords: Bloom’s Taxonomy, lesson planning, cognitive skills, critical thinking, classroom strategies
Bloom’s Taxonomy can be a powerful tool to transform teaching and learning. By design, it focuses attention on the cognitive work students do. This shifts planning from only content and procedures to the kinds of thinking students will demonstrate and how you will see evidence of that thinking.
For decades, reform has centered curriculum, standards, and assessment. Bloom’s reframes the work by foregrounding thinking, transfer, and intellectual growth.
Want a foundational overview first? See What Is Bloom’s Taxonomy?.
Bloom’s Taxonomy: Planning Moves at a Glance
| Level | Teacher Move | Student Response |
|---|---|---|
| Remember | Retrieve essential facts to reduce cognitive load. | List, label, match, identify key ideas. |
| Understand | Check meaning and clarify relationships. | Explain, summarize, restate in their own words. |
| Apply | Give learners a context to use ideas. | Demonstrate, solve, illustrate with examples. |
| Analyze | Prompt comparison, patterns, causes, parts. | Differentiate, categorize, compare approaches. |
| Evaluate | Ask for judgments supported by criteria. | Critique, justify, defend a position with evidence. |
| Create | Invite new products, solutions, or models. | Design, propose, produce, or transform ideas. |
Tip: Begin with lower levels to establish understanding, then intentionally move upward to support analysis, reasoning, and transfer.
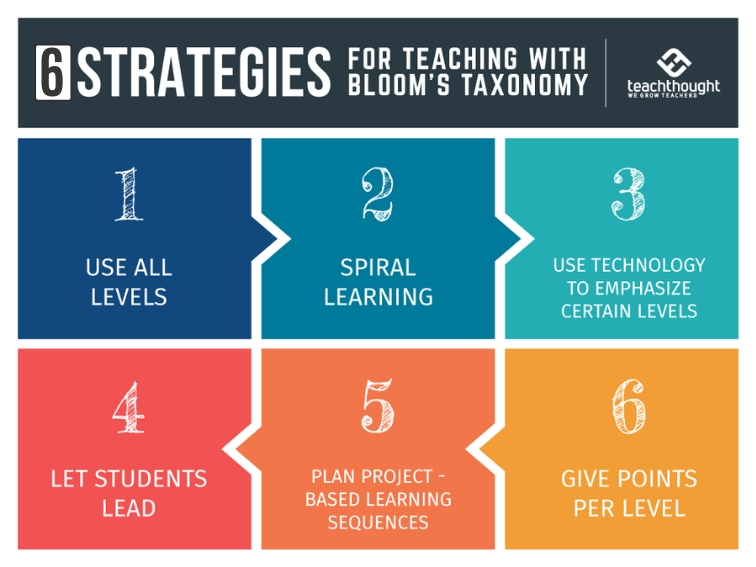
Six Strategies For Teaching With Bloom’s Taxonomy
1. Use Every Level
Lower levels like recall and define are not “bad.” They reduce cognitive load and help students move fluidly into higher level thinking and transfer. The larger a student’s mental library, the easier it becomes to analyze, evaluate, and create with confidence.
Example: In a biology lesson on cells, students first label cell parts (remember), explain each function (understand), and then design a simple model demonstrating how organelles work together (create).
2. Use Bloom’s Spiraling
Move learners upward intentionally. Begin with recall and explanation, then work toward comparison, evaluation, and creation. This can frame lessons, discussions, assessments, or project based learning sequences.
Example: In a civil rights unit, students identify key figures (remember), explain major events (understand), compare strategies across movements (analyze), and propose a modern civic action plan (create).
3. Use Technology To Emphasize Specific Levels
Digital tools can extend or limit thinking. Design tasks where learners generate, remix, critique, and publish. For help mapping digital verbs, see Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy and Bloom’s Digital Verbs.
Example: Students use a public data dashboard to compare pollution levels (analyze) then produce a short podcast recommending solutions supported by evidence (create).
4. Let Students Lead
Invite learners to choose media, topics, or questions while you guide the cognitive level. This builds ownership and makes advanced thinking feel accessible and concrete.
Need verbs to support student planning? See Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs.
Example: During a literature study, students choose whether to analyze themes through a visual essay, short film, or podcast while you prompt evaluation and comparison.
5. Plan Project Based Learning Sequences
Use Bloom’s to map PBL. Begin with defining and describing, then evaluate ideas and design original solutions or products. Bloom’s supports iteration, revision, and transfer.
Example: In a recycling project, students define the problem (remember), research the system (understand), identify inefficiencies (analyze), evaluate existing solutions (evaluate), and design an initiative to reduce waste (create).
6. Give Points Per Level
To encourage movement, you can award points for contributions at different levels. Begin balanced, then reduce points for staying only at recall or description. The goal is upward thinking, not ranking.
Example: In a Socratic seminar, students earn points for moving from clarifying facts to analyzing motivations to proposing an alternate ending with textual evidence.
Conclusion
Teaching with Bloom’s means foregrounding thinking rather than treating it as a byproduct. Use every level. Spiral intentionally. Integrate thoughtful digital tasks. Invite student leadership. Design projects that build toward creation and reasoning. This is how Bloom’s becomes more than a poster and instead a planning and thinking framework for inquiry.
Reference
- Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy: An Overview. Theory Into Practice, 41(4), 212–218.