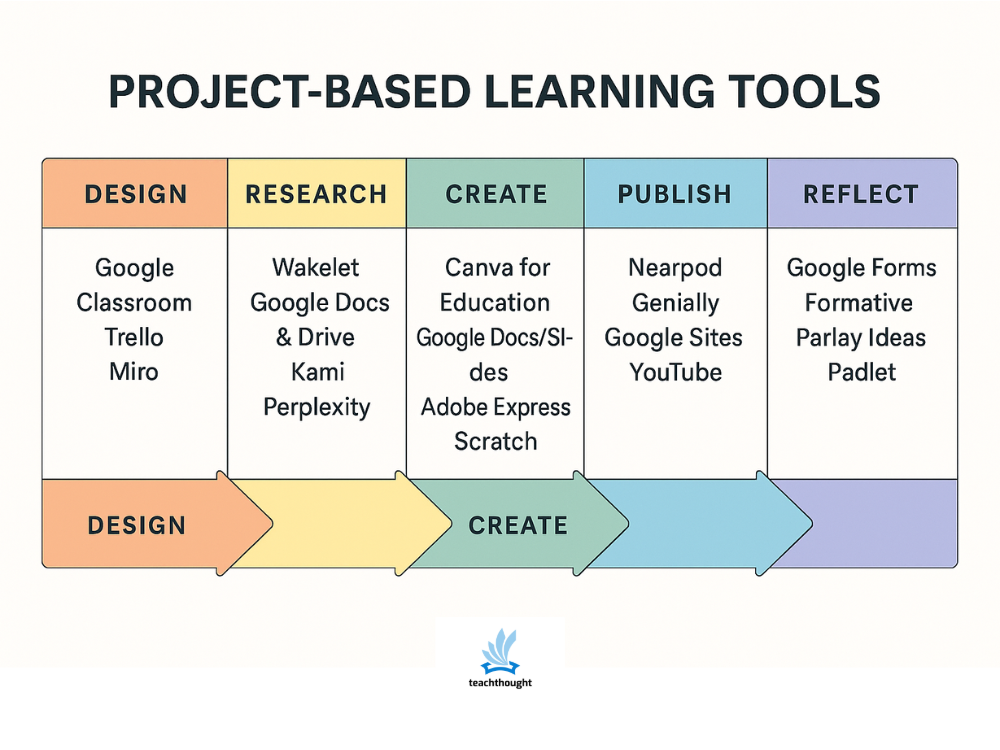
Project-Based Learning Tools
by Terry Heick
Meta description: A practical guide to classroom technology that supports project-based learning, organized by how tools help students plan, research, create, publish, and reflect on projects.
Project-Based Learning is an established approach to learning that acts both as a curriculum and instruction tool, as well as a new way for students to think about school. (See What Does The Research Say About Project-Based Learning?)
Rather than strictly academic lessons and units, real-world problems can be solved, and students gain experience with long-term management of the learning process, and the possibility of self-direction.
Project-Based Learning allows the natural embedding of “school” in authentic environments, whether digital or physical. It is a way of learning that is as much about the process as the project, allowing for the seamless integration of technology and the inclusion of digital and social media to solve relevant personal and social challenges.
In this post, tools are organized by how they support the work of PBL in the classroom: designing projects, supporting inquiry, creating and revising products, publishing student work, and helping students reflect on what they learned.
See also: Examples of Project-Based Learning and Phases Of Project-Based Learning.
Design & Plan Projects
These tools help teachers and students structure project work, clarify expectations, and manage timelines. They are useful for posting project briefs, organizing tasks, and keeping groups aligned on deadlines and responsibilities.
| Tool | What it does in PBL | Typical classroom use |
|---|---|---|
| Google Classroom | Central hub for project instructions, resources, and submissions. | Post the project overview, rubric, checkpoints, and final submission tasks for each group. |
| Trello | Visual task board for organizing project steps and tracking progress. | Create columns such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done” and assign cards to group members. |
| Miro | Collaborative whiteboard for mapping ideas, timelines, and workflows. | Use project canvases for driving questions, milestones, and group responsibilities. |
Research & Inquiry
These tools support students as they investigate driving questions, gather sources, and organize information. They can help students move from broad topics to focused, answerable questions and keep track of what they find.
| Tool | What it does in PBL | Typical classroom use |
|---|---|---|
| Wakelet | Curates links, videos, and notes into collections. | Have groups save and organize research sources for their project in a shared collection. |
| Google Docs & Drive | Shared space for notes, source lists, and draft outlines. | Use a shared document for driving questions, key sources, and running notes. |
| Kami or Diigo | Tools for highlighting, annotating, and commenting on texts. | Ask students to annotate articles or PDFs and tag evidence they might use in their projects. |
| Perplexity | AI-assisted tool for finding and summarizing information. | Model how to use AI tools to clarify questions, compare sources, and cross-check claims. |
Create & Collaborate
These tools support the work of building products, revising drafts, and collaborating with peers. They are used when students are actively creating, revising, and combining their work into a final product.
| Tool | What it does in PBL | Typical classroom use |
|---|---|---|
| Canva for Education | Designs visual products such as posters, reports, and presentations. | Have students design infographics, one-page reports, or slide decks to communicate findings. |
| Google Docs / Slides | Shared writing and presentation tools for real-time collaboration. | Use shared documents for drafting reports and co-creating presentations in real time. |
| Adobe Express | Creates videos, graphics, and web pages with templates. | Ask students to produce short explainer videos or simple project pages. |
| Scratch | Block-based coding platform for interactive stories and simulations. | Have students build simple simulations or interactive stories that model concepts from the project. |
| Minecraft Education Edition | Sandbox environment for building models and environments. | Use worlds to model historical settings, design sustainable cities, or prototype solutions. |
Publish & Present
These tools help students share their work with classmates, families, or wider audiences. They are useful for final presentations, exhibitions, and digital showcases.
| Tool | What it does in PBL | Typical classroom use |
|---|---|---|
| Nearpod | Interactive presentation tool with embedded questions and media. | Have students present their findings with embedded questions to check peer understanding. |
| Genially | Creates interactive presentations, infographics, and simple microsites. | Use for gallery-style displays where each group presents an interactive visual summary of their project. |
| Google Sites | Lightweight platform for project pages or digital portfolios. | Have each group build a short project page with an overview, media, and reflections. |
| YouTube (class channel) | Hosts student-created videos for broader audiences. | Publish final video products and embed them in your LMS or class website. |
Reflect & Assess
These tools support ongoing reflection, peer feedback, and assessment of both the process and the final product. They are useful for check-ins during the project and for closing the loop at the end.
| Tool | What it does in PBL | Typical classroom use |
|---|---|---|
| Google Forms | Collects quick check-ins, self-assessments, or exit tickets. | Create simple reflection forms for groups at major checkpoints. |
| Formative | Platform for delivering tasks and seeing responses in real time. | Use short tasks to see how well students understand key concepts during the project. |
| Parlay Ideas | Structures discussions and peer feedback. | Host written or live discussions where students respond to each other’s project ideas or findings. |
| Padlet | Shared board for collective reflection and peer comments. | Create columns for “What went well,” “What was challenging,” and “Next time we will…” and have groups post responses. |
| Seesaw | Portfolio and reflection tool, especially for younger learners. | Have students upload photos, videos, or audio reflections that document their project process. |
Using Technology In Project-Based Learning
Technology in project-based learning should support the design of meaningful projects, not replace it. The most useful tools make it easier for students to plan, investigate, create, share, and reflect without overwhelming the work itself.
When choosing tools, start with the project: what students are trying to understand, who the work is for, and how they will show what they know. Then select a small set of tools that help them do that work more clearly and collaboratively.
For a broader overview of classroom technology, see Essential EdTech Tools For The Classroom.