What Is Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Learning Theory?
According to Vygotsky, learning and development are inseparable from the social and cultural contexts in which individuals participate.

According to Vygotsky, learning and development are inseparable from the social and cultural contexts in which individuals participate.
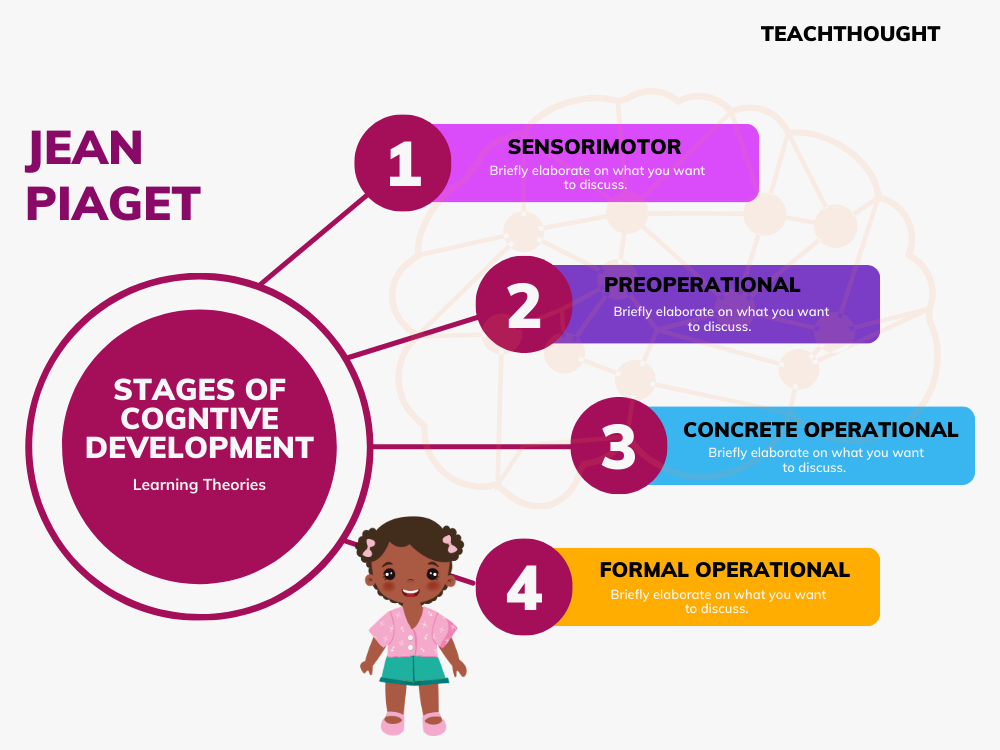
Piaget’s stages of cognitive development include the sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational stage.
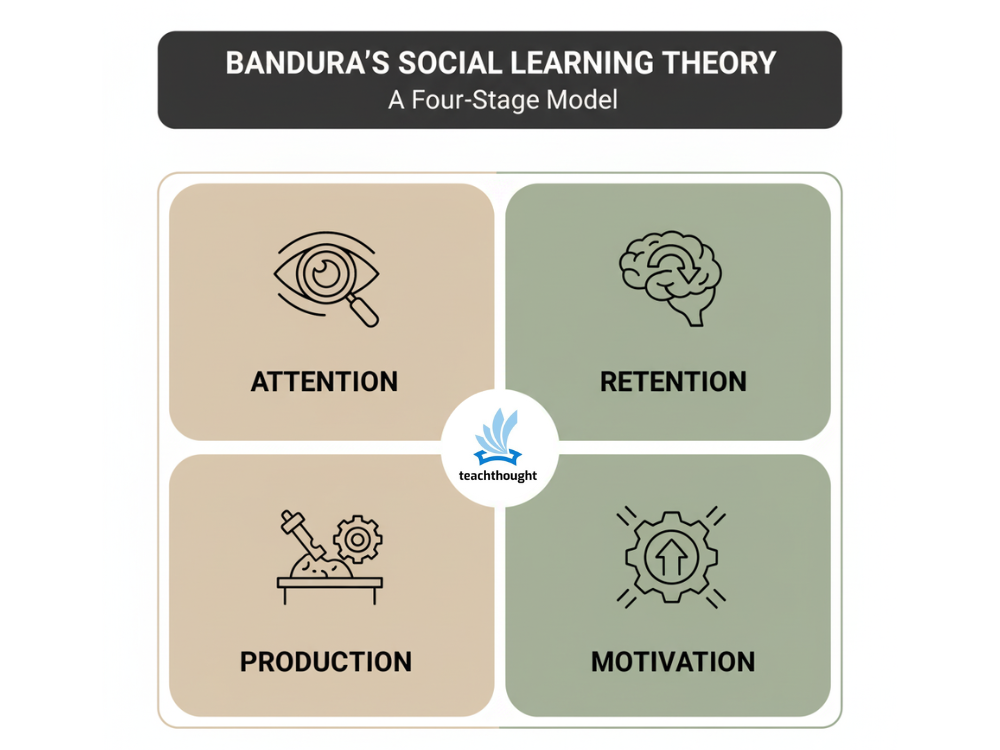
Bandura’s Social Learning theory explained that children learn in social environments by observing and then imitating the behavior of others.

Constructivism focuses on how learners construct knowledge through experience while constructionism emphasizes learning by making.
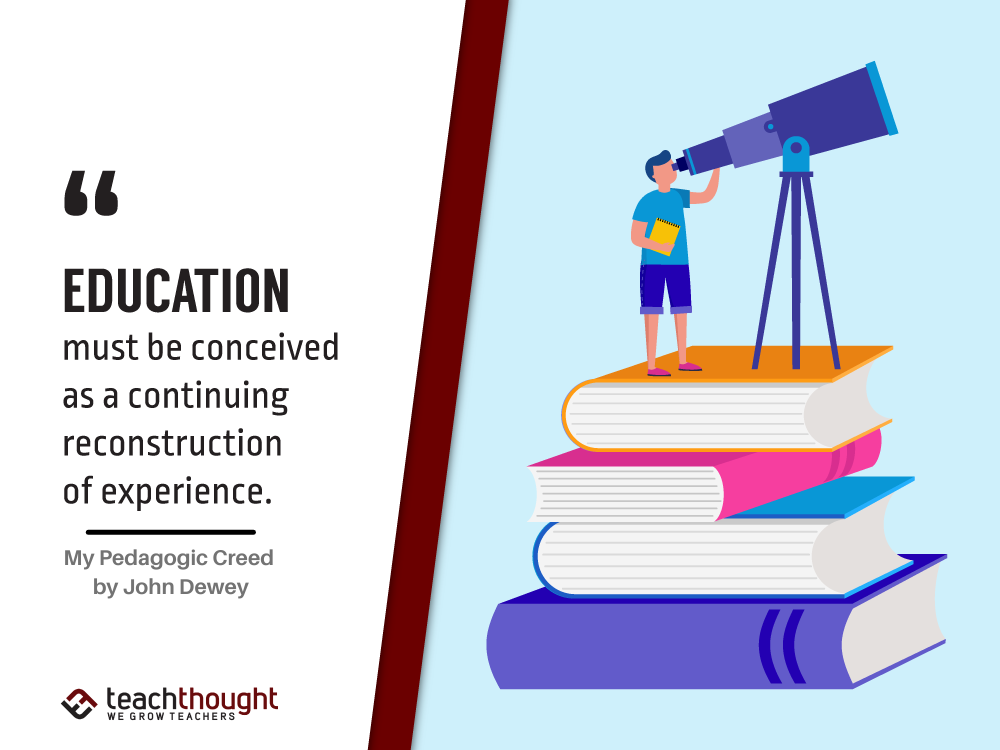
Dewey believed that learning was socially constructed and that brain-based pedagogy should emphasize active, experiential learning.
From Constructivism and Connectivism to Situated Learning, here are 32 of the most common learning theories every teacher should know.
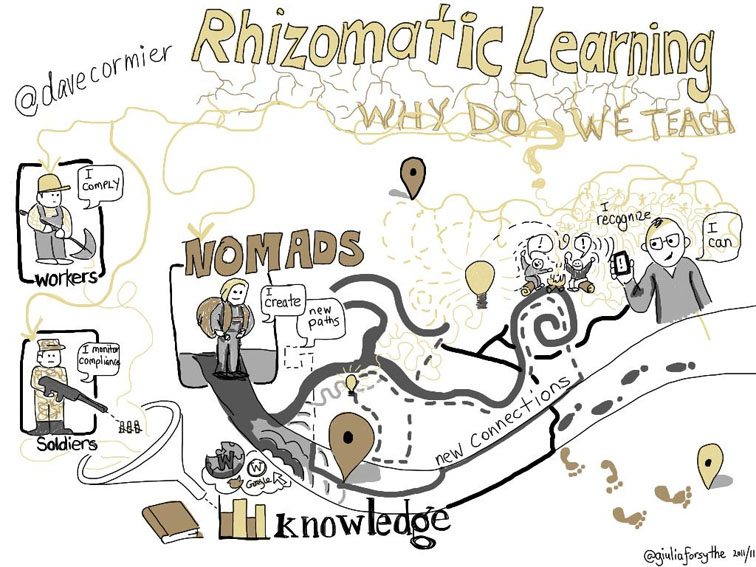
Rhizomatic Learning embraces the beautiful complexity of the human experience, and the unpredictability of the learning process.

The frequency of repetition and rehearsal, if spaced at intervals, promotes better recall of memory than if presented in one long burst.
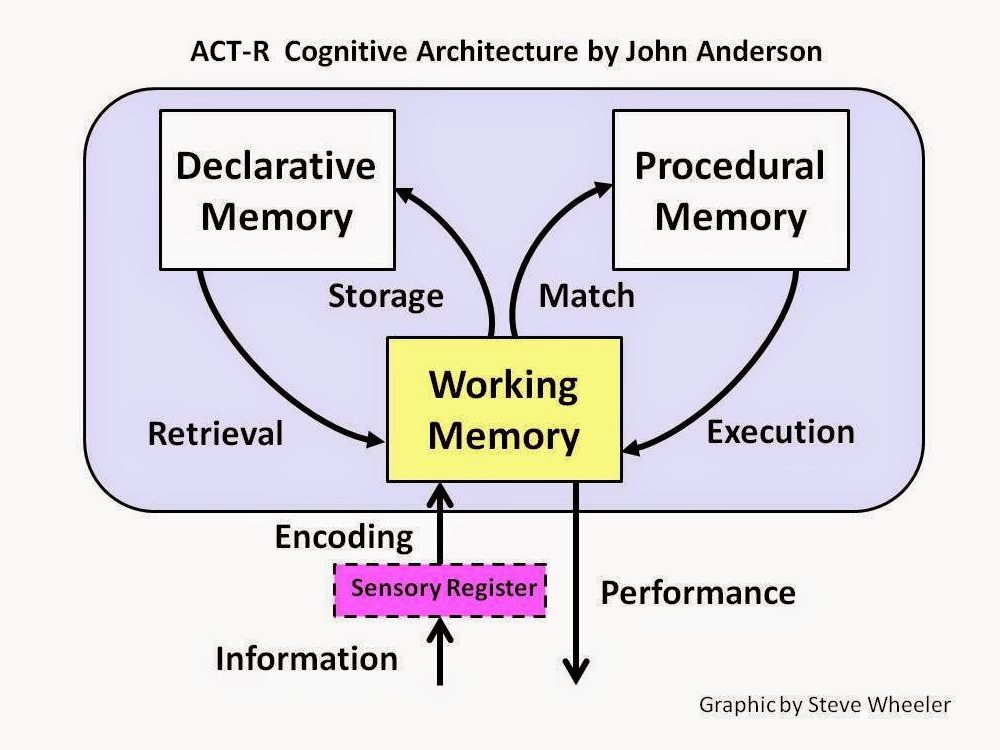
ACT-R is a way of specifying how the brain itself is organized in a way that enables individual processing modules to produce cognition.
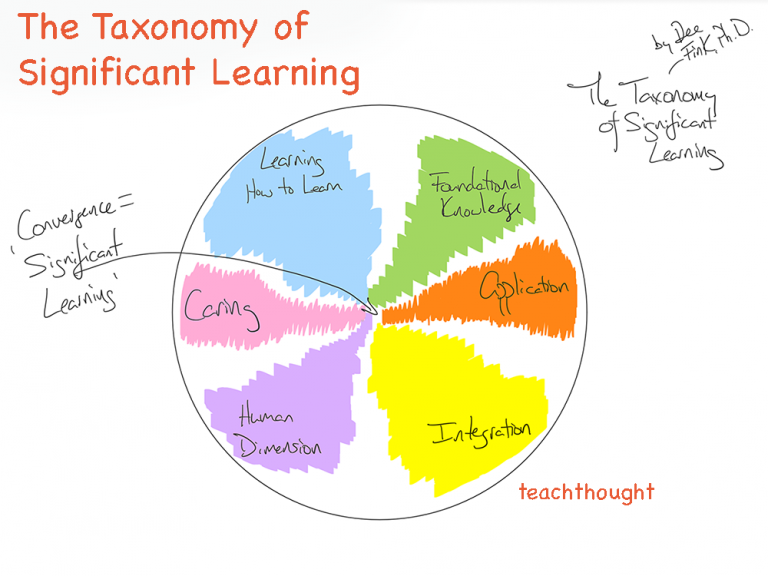
The Taxonomy Of Significant Learning is useful for making design considerations for student learning experiences.
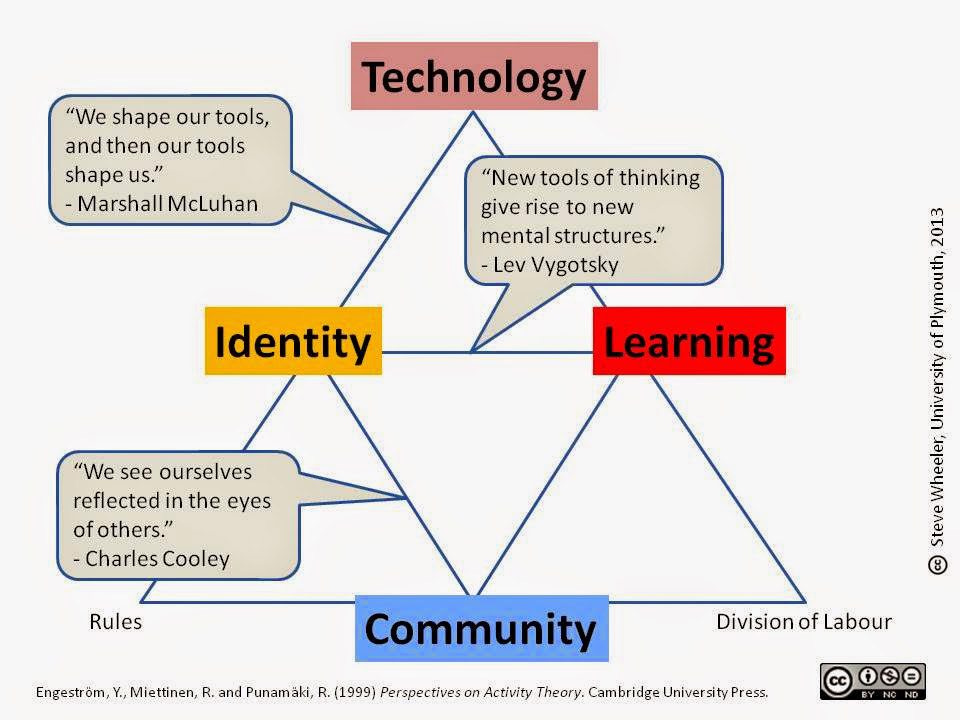
Students need incremental challenges they can engage with at a social level so the entire community of learners can collaborativelay meaning.

Three Levels Of Information Processing by Steve Wheeler, Associate Professor, Plymouth Institute of Education This is number 5 in my blog series on major learning theories. My plan is to work through the alphabet of psychologists and provide a brief overview of their theories, and how each can be applied in education. In the last post we…

Bruner believed that when children start to learn new concepts, they need help from teachers and other adults in the form of active support.
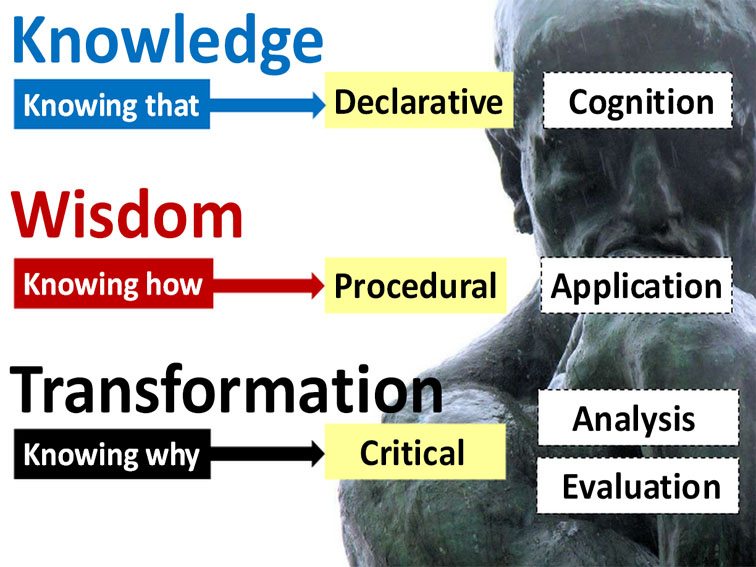
Learning is changing–becoming more entrepreneurial than directly didactic. That is, more learner-centered and than teacher-controlled.