Tag: Brain-Based Learning Resources
4 Neurosystems Of Learning
It is suggested that the brain does not have one learning system but four–each with its own unique memory pattern and accompaniments.
How The Brain Works–And How Students Can Respond
3 major brain elements help control what information your brain takes in: the reticular activating system, limbic system, and dopamine.
Examples Of Brain-Based Assessment
Ideally, assessments correspond to teaching that promotes creativity, analysis, judgment, expert thinking, and complex communication.
8 Ways To Create A Brain-Friendly Classroom
How can you create a brain-friendly classroom? By reducing stress, creating positive associations, and promoting feedback loops.
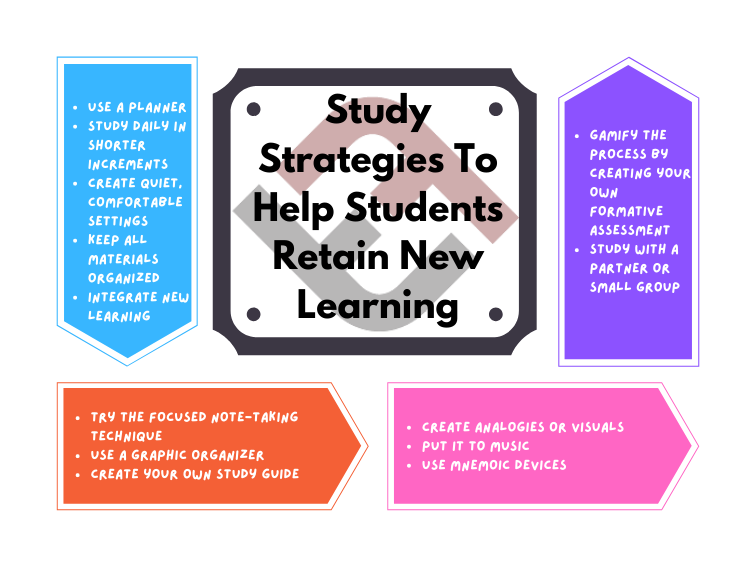
13 Study Strategies To Help Students Retain New Learning
Studying is often viewed as a means to an end. We hope these study strategies help learners realize that it is a…
What Are The Primary Human Drives?
In outlining this theory, Rifkin provides four fundamental human needs culminating in a ‘first drive’: the drive to belong.
6 Simple Ways To Reduce Student Stress In The…
The research is clear that reducing student stress can have a profound effect on learning. A big part of this? Clear and…
How The Memory Works In Learning
How does the memory work in learning? The more times an action is repeated, the more dendrites grow and interconnect.