How To Connect An iPad To A Smartboard [Updated]
By displaying the iPad on the projector, you’ve got an easy way to broadcast your screen–or a student’s screen–to the entire class.

By displaying the iPad on the projector, you’ve got an easy way to broadcast your screen–or a student’s screen–to the entire class.

Nearly every major educational institution in the world is teaching with YouTube through videos featuring news, lectures, and courses.
Social media can significantly distract students, leading to procrastination and reduced focus on academic tasks.
Schools operating through a Mac do not have complete immunity from malware.

Every student has unique learning needs, and Canberra families have a wide range of tutoring options available.

When the first public genome browsers appeared in 2001, everything was pre-rendered server-side.
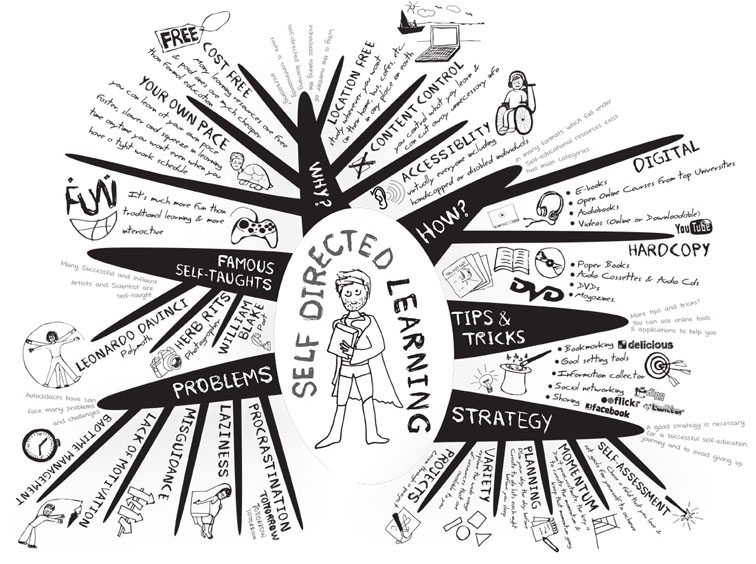
Modern access to information and learning platforms make self-directed learning more accessible–and powerful–than ever before.

Despite good intentions, the way we approach ‘career readiness’ in education often falls short.

Let’s stop the endless worksheets and cooperative groups that skim through text merely to find answers and grow a culture of reading.

Costa’s levels of questioning feature three tiers of questioning designed to promote higher level thinking and inquiry.
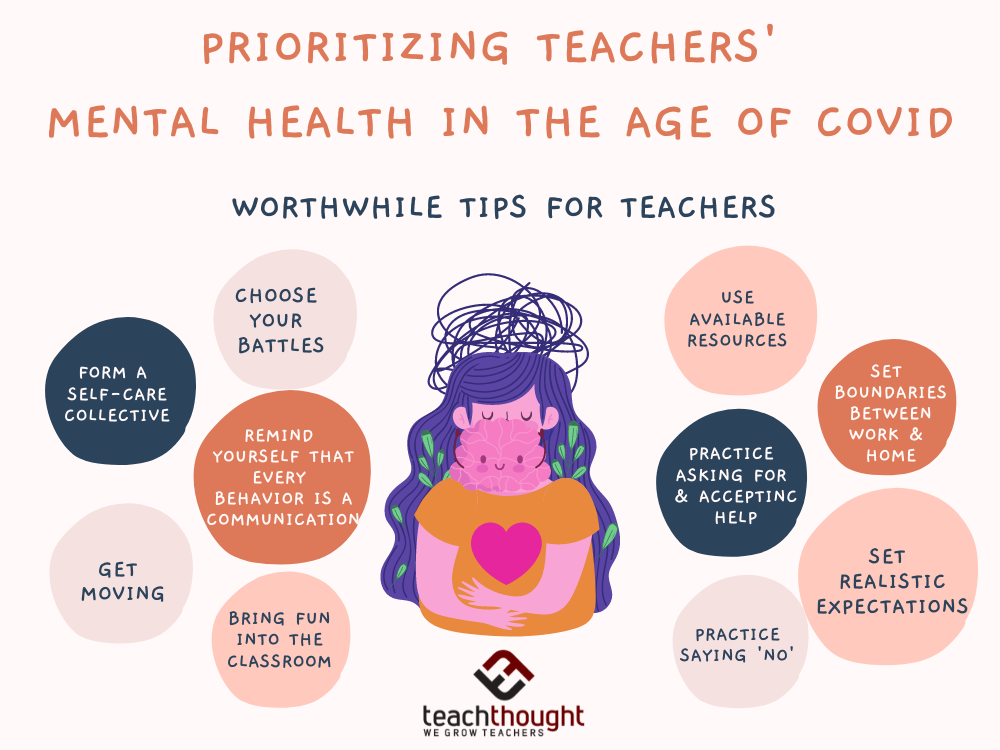
We can’t control everything and apologizing for things out of our control can set unrealistic expectations of teachers.

From Khan Academy to Canva, these 25 apps make informal learning practical and engaging—ideal for Genius Hour, self-directed projects, or personal growth.
Curated Design Thinking Resources for Educators A Curated List of Design Thinking Resources for Educators Educators and students at all levels are using design thinking to create solutions for real-world problems. Whether you’re new to the concept or looking for fresh ideas, this updated and curated list features high-quality resources that are free, low-cost, or…

10 TED Talks to Elevate Your Communication Skills Effective communication isn’t just about speaking clearly — it’s about connecting deeply. These ten hand-picked TED Talks explore empathy, storytelling, human connection, digital communication, and the power of listening. Watch, reflect, and apply these ideas to sharpen how you speak, listen, and build meaningful dialogue. Elizabeth Lesser…